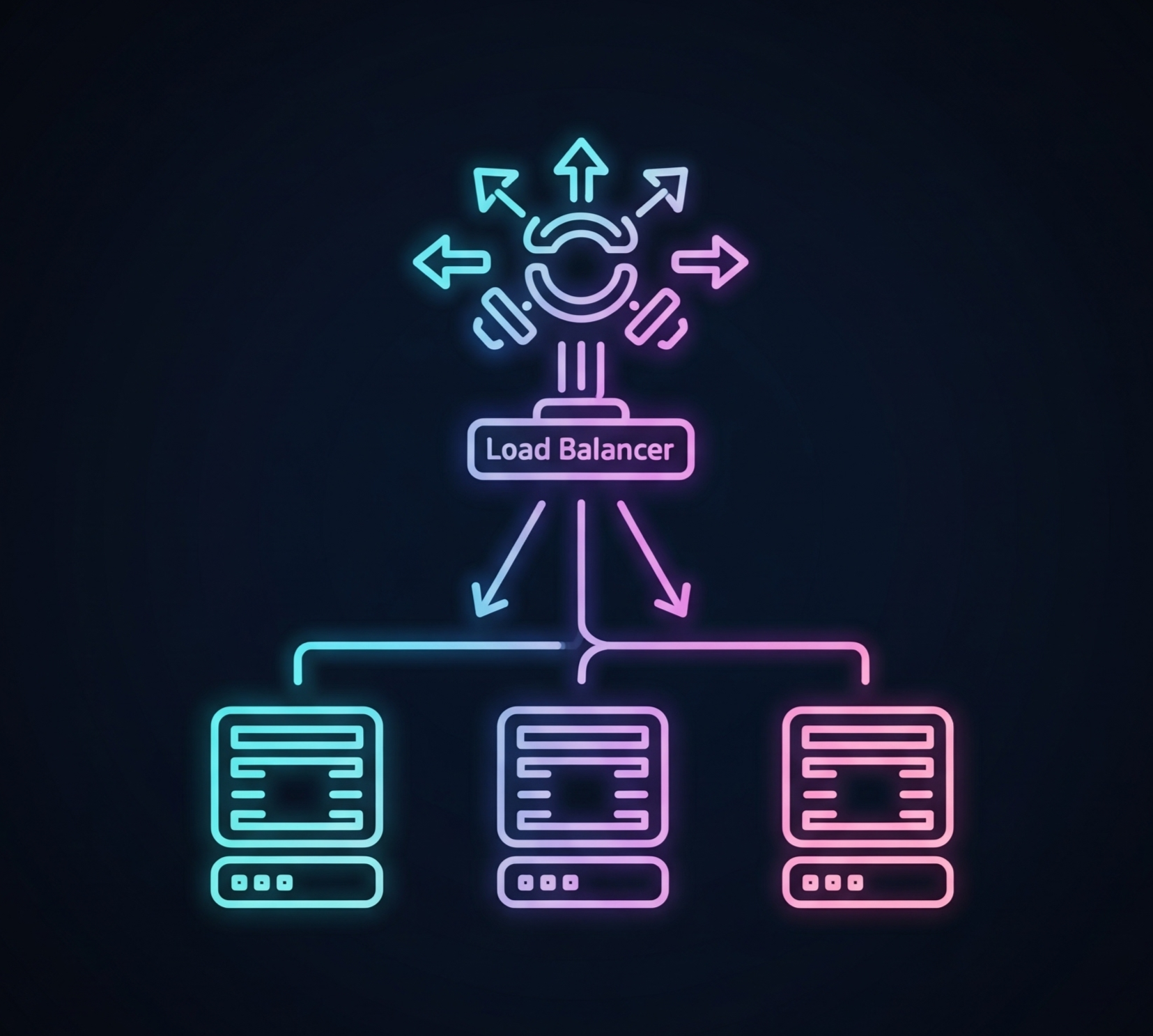
What is Load Balancing?
A load balancer is a device or software that distributes network traffic across multiple servers to ensure no single server is overloaded. The provided guide outlines how to create a load-balanced web server architecture using VirtualBox, Ubuntu, HAProxy, and Nginx. This setup is designed to distribute incoming requests, ensuring continuous service and optimizing resource utilization.
The primary function of a load balancer, as demonstrated in the guide, is to intelligently distribute traffic to multiple web servers. This process achieves several key goals for a robust and scalable backend system.
Key Benefits
- **Increases Reliability and Availability:** If one server fails, the load balancer can redirect traffic to the remaining healthy servers, preventing service interruptions.
- **Enhances Performance:** By spreading the load, it prevents a single server from becoming a bottleneck, which leads to faster response times for users.
- **Improves Scalability:** It allows you to add more servers to your setup to handle increased traffic without affecting performance. The guide provides an example of this by configuring HAProxy to balance traffic across three web servers.
Technologies & Conceptual Stack
- **Load Balancer:** The document uses HAProxy, a high-performance open-source load balancer. Alternatives could include Nginx or cloud-based solutions like AWS Elastic Load Balancer.
- **Web Server:** The guide uses Nginx. For a Node.js stack, the web server would be a Node.js application running on a specific port.
- **Application/Database:** The document mentions that you could expand the setup with Node.js apps and databases, indicating that this is where you would integrate those specific technologies.
Challenges & Learning
Developing this system involved understanding inter-process communication, managing shared resources, and implementing strategies for fault tolerance. It significantly deepened my knowledge of Node.js concurrency and backend architecture best practices.